UI/UX
Fitt’s Law

Fitts’ law is a projecting model or medium of human movement primarily used in human–computer interaction and ergonomics. Fitts’ law is traditionally used as a behavioral measurement for usability assessments by correlating a user’s response time with an index of difficulty measurement. Generally, Fitts’ law has two components:
1) A target acquisition task and measures to assess both the number of bits of information transmitted, called Index of Difficulty (ID), and
2) The rate of transmission, called Index of Performance. Index of performance is more recently referred to as throughput (TP).
Fitts’ Law has its roots in Information Theory. In studying Shannon’s Theorem which describes the effective information capacity of a communications channel (Shannon, 1948), Fitts’ (1954) attempted to formulate a similar equation for human channel capacity. Fitts’s Law provides a model of human movement, established in 1954 by Paul Fitts, which can accurately predict the amount of time taken to move to and select a target. This scientific law predicts that the time required to rapidly move to a target area is a function of the ratio between the distance to the target and the width of the target.
In recent literature, Fitts’ law is primarily used in two ways:
1) To predict human movement time when moving from one target to another
2) To compare and evaluate the quality of various input devices. For the purposes of assessing the applicability of Fitts’ law to gesture based input methods, it is important to focus on the use of Fitts’ law to compare and evaluate input devices.
In layman’s terms: the closer and larger a target, the faster it is to click on that target. This is easy to understand, not too difficult to implement and it doesn’t seem to make much sense to contradict such a simple medium and obvious statement.
Fitts’ original formula was based on Shannon’s theorem (Shannon, 1948).
Mathematically it can be written as
MT = a + b log 2 ( 2A / W )
MT : Movement time (average) taken to complete the movement or point the target
a : Start / Stop time of the device (y intercept)
b : Inherent speed of the device (slope of line)
W : Width of the target measured along the axis of motion, which corresponds to accuracy
A : Distance from the starting point to the center of the target
The term log 2 ( 2A / W ) is called the index of difficulty (ID). It describes the difficulty of the motor tasks. 1/b is also called the index of performance (IP) and measures the information capacity of the human motor system.
Thus MT= a+b ID = a + ID / IP
Within the field of Human Factors Engineering, Fitts’ law is a prominent mathematical model used to evaluate the effectiveness of pointing devices. It states that the time required to move from one target area to a second target area is a function of the size of the target and the distance to the target. Since the introduction of the computer, Fitts’ law has been used primarily to test input devices for pointing and selecting. ISO standards establish a means for evaluating task precision with various input modalities using a target acquisition task and measures of throughput and index of difficulty established by Paul Fitts. Today, engineers and designers of input modalities typically refer to the International Standards Organization’s (ISO) standards as the means for determining “good usability”. (ISO/TS 9241-411, 2012). This is now known as Fitts’ Law and its effectiveness has been demonstrated in hundreds of studies from its establishment in 1954 for both one- and two- dimensional operations.
80,175 total views, 3 views today
Design
Haptic technology its potential to enhance user experience

Haptic technology refers to technology that provides tactile feedback to users, allowing them to interact with digital devices and environments in a more immersive and intuitive way. Haptic technology is based on the sense of touch and uses vibration, pressure, or other physical stimuli to convey information and sensations to the user. This can range from simple vibrations in response to touch input on a smartphone screen to complex, multidimensional haptic feedback in virtual reality or gaming applications.
The goal of haptic technology is to create a more natural and intuitive interaction between people and technology, allowing users to “feel” the digital world in a way that mimics the physical world. Haptic technology is used in a variety of devices and applications, including smartphones, game controllers, wearable devices, and medical devices, among others. In virtual reality and augmented reality applications, haptic technology can be used to simulate the feeling of touching virtual objects and environments, making the experience more immersive and believable.
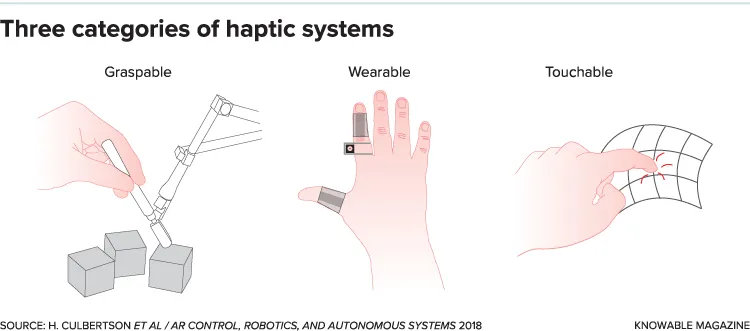
Haptic technology is still an emerging field, and there is ongoing research and development aimed at improving the accuracy, versatility, and durability of haptic devices. As technology continues to advance, it is likely that haptic technology will become increasingly integrated into a wide range of devices and applications.
Haptic technology has the potential to significantly impact various industries and immersive experiences. Some of the ways in which haptic technology is being used or has the potential to be used include:
- Gaming and Virtual Reality: Haptic technology can enhance the realism of gaming and virtual reality experiences by allowing players to feel the impact of explosions, collisions, and other events in real-time.
- Smartphones and Wearables: Haptic technology is commonly used in smartphones and wearables to provide tactile feedback for touch inputs, such as tapping or scrolling. This enhances the overall user experience and makes it easier for people to use these devices.
- Healthcare: Haptic technology is being used in the healthcare industry for rehabilitation and prosthetics, allowing patients to experience touch sensations in a controlled and precise manner.
- Automotive: Haptic technology is being used in the automotive industry to enhance the driving experience. For example, haptic feedback can be used to alert drivers to safety warnings, such as lane departure warnings, or to provide a more immersive experience when using in-car entertainment systems.
- Manufacturing: Haptic technology is being used in the manufacturing industry to provide workers with information and feedback in real-time, allowing them to work more efficiently and safely.
The use of haptic technology has the potential to greatly enhance the user experience in a wide range of industries and immersive experiences, making interactions with digital devices and environments more intuitive, engaging, and realistic.
1,980 total views, 2 views today
Design
Trends of UX 2023

User experience (UX) is a rapidly evolving field that is constantly influenced by new technologies and trends. As we move into 2023, there are a number of key trends that are expected to shape the field of UX. The field of user experience (UX) is constantly evolving, and new trends and technologies are emerging all the time. Here are a few trends that are expected to be prevalent in 2023:
- Emphasis on Empathy: With the increasing awareness of mental health and well-being, there is a growing emphasis on designing products and services that take into account the emotional needs of users. This includes designing for empathy, which involves understanding and addressing the emotional needs of users. This is achieved by conducting user research and testing, using tools like user interviews and surveys, and observing users’ behavior and emotions as they interact with a product or service.
- Human-centered design: The shift in focus towards human-centered design, which puts users at the center of the design process, will continue to be a prominent trend in 2023. This approach puts users at the center of the design process, and allows designers to create products and services that better meet the needs and goals of users. Human-centered design is achieved by conducting user research, testing, and validation to understand users’ needs, goals and pain points, and using this information to design the product or service. This approach allows designers to create products and services that better meet the needs and goals of users.
- Voice-based interfaces: With the increasing popularity of voice assistants like Alexa and Google Home, voice-based interfaces are becoming an increasingly important aspect of UX. Voice-based interfaces are also expected to become increasingly important in 2023. Voice-based interfaces are expected to be used in more products and services as a means of interaction, and designers will need to consider how to design voice-based interfaces that are intuitive, easy-to-use, and accessible to all users.
- Personalization and customization: With the rise of big data and artificial intelligence, it’s becoming increasingly possible to personalize and customize products and services to meet the needs of individual users. In 2023, we can expect to see more products and services that are tailored to the unique needs and preferences of users. With the rise of big data and artificial intelligence, it’s becoming increasingly possible to personalize and customize products and services to meet the needs of individual users. Designers will need to consider how to use data and AI to create personalized experiences that meet the unique needs and preferences of users.
- Micro-interactions: Micro-interactions, such as subtle animations and sound effects, are becoming increasingly important in creating a more engaging and satisfying user experience. In 2023, we can expect to see more products and services incorporating micro-interactions to enhance the overall user experience. Micro-interactions, such as subtle animations and sound effects, are also becoming increasingly important in creating a more engaging and satisfying user experience. In 2023, designers will need to consider how to use micro-interactions to enhance the overall user experience.
- Privacy and security: Finally, privacy and security are becoming increasingly important as users become more concerned about how their personal information is being used and protected. With the increasing concern about data privacy and security, it’s becoming increasingly important for designers to consider how products and services protect the personal information of users and how to communicate this to users in a clear and transparent way.
The field of UX is constantly evolving and designers need to keep abreast of the latest trends and technologies to create products and services that meet the needs and goals of users. By understanding and addressing the emotional needs of users, and by using human-centered design, voice-based interfaces, personalization, micro-interactions and privacy and security, designers can create products and services that provide a positive and efficient user.
2,590 total views, 6 views today
Technology
Driving the development of NLP

Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a rapidly growing field of artificial intelligence (AI) that is having a significant impact on various industries, including healthcare, technology, and lifestyle and there are some key technologies and techniques that are driving the development of NLP and are being applied in real-world applications.
One of the key technologies driving the development of NLP is deep learning. Deep learning algorithms, such as recurrent neural networks (RNNs) and transformer models, are being used to improve the accuracy and efficiency of NLP tasks, such as language translation, sentiment analysis, and text summarization. For example, RNNs and transformer models can be used to analyze large amounts of text data and identify patterns and trends that can assist in diagnoses and treatment planning in healthcare. Additionally, transformer models such as BERT and GPT-3 are used to improve the performance of virtual assistants and customer service chatbots.
Another important technology driving the development of NLP is the use of large-scale pre-trained models. Pre-trained models, such as BERT, GPT-3, and T5, have been trained on large amounts of text data and can be fine-tuned for specific NLP tasks, such as question answering and text classification. These pre-trained models have significantly improved the performance of NLP tasks and have made it easier for developers to build and deploy NLP applications. Deep learning and pre-trained models, other key technologies and techniques that are driving the development of NLP include:
- Named Entity Recognition (NER): used to identify and classify named entities, such as people, organizations, and locations, in text data.
- Part-of-Speech Tagging (POS): used to identify and classify the parts of speech, such as nouns, verbs, and adjectives, in text data.
- Sentiment Analysis: used to determine the emotional tone of text data, such as whether a piece of text is positive, negative, or neutral.
- Text Summarization: used to generate a condensed version of text data, such as a summary of a news article or a summary of customer feedback.
As the field of NLP continues to evolve, it will likely play an increasingly important role in shaping the way we live, work, and interact with technology. NLP is a rapidly growing field of AI that is having a significant impact on various industries, including healthcare, technology, and lifestyle. Key technologies and techniques, such as deep learning, pre-trained models, and NER, POS and Sentiment Analysis are driving the development of NLP and are being applied in real-world applications to improve efficiency, accuracy, and communication.
1,802 total views, 2 views today
-

 Editor's Picks6 years ago
Editor's Picks6 years agoThe Ontology of Designing Self
-

 Science6 years ago
Science6 years agoHuman Cognition Processes And Types
-

 Design8 years ago
Design8 years agoDon Norman’s Principles of Design With Examples
-

 Design8 years ago
Design8 years agoJakob Nielsen’s (Usability Heuristics): 10 Heuristic Principles With Examples
-

 Design7 years ago
Design7 years agoGamification Explained And How to Gamify Your Daily Life Part 2 of 2
-

 Editor's Picks7 years ago
Editor's Picks7 years agoLost in the Woods
-

 Design7 years ago
Design7 years agoHuman Factors, Ergonomics and Design
-

 Art7 years ago
Art7 years agoHistory of Typography-Part 3 of 3



