UI/UX
User Interface (UI) Principles

Let’s start with the fundamentals of user interface design. Constantine and Lockwood describe a collection of principles for improving the quality of your user interface design.
1.The structure principle
Your design should organize the user interface purposefully, in meaningful and useful ways based on clear, consistent models that are apparent and recognizable to users, putting related things together and separating unrelated things, differentiating dissimilar things and making similar things resemble one another. The structure principle is concerned with your overall user interface architecture.
Users want you to fill their needs.
- Use the most appropriate page layout. Consider the spatial relationship between items on the page and structure them according to their importance. The most important items should be easily accessible. Appropriate placement draws attention to the most relevant pieces of information and improves readability.
- Design strategically. You can manipulate user`s attention using colour, light, contrast, and texture.
2.The simplicity principle
Your design should make simple, common tasks simple to do, communicating clearly and simply in the user’s own language, and providing good shortcuts that are meaningfully related to longer procedures.
Users like to speak (and read) in their language.
- Use appropriate language.
All interfaces require copywriting. Provide clear labels for actions and keep your messages simple, not lengthy. Users will appreciate it because they like to communicate effectively. - Use font type setting to create hierarchy and clarity.
Don’t forget that people read 2 or 3 words at a time. Various sizes, fonts, and arrangement of the text will help to increase scanability, legibility and readability of your pages or screens.
3.The visibility principle
Your design should keep all needed options and materials for a given task visible without distracting the user with extraneous or redundant information. Good designs don’t overwhelm users with too many alternatives or confuse them with unneeded information.
Users don’t like surprises.
- Be consistent. Use mutual elements and create consistency of your UI. Users feel more comfortable and can operate quickly when they can find familiar elements and patterns. Besides, the interface should keep the same patterns across languages, layouts, elements, colours and fonts throughout the different pages or screens to help facilitate efficiency.
- Help your users to learn your product. The consistency of UI and using mutual patterns help your users learn easier. When they figure out how to use one part of the product they can apply these skills to other parts.
4.The feedback principle
Your design should keep users informed of actions or interpretations, changes of state or condition, and errors or exceptions that are relevant and of interest to the user through clear, concise, and unambiguous language familiar to users.
Users like being confident.
- Communicate with users when they to do something right.
Interface should always speak to users when their actions are not only wrong or misunderstood but also when they are right and help go forward. Users should be proud and feel confident. - Don’t be annoying.
Do you remember that the users’ research is the first step of user interface design? UI shouldn’t annoy your target audience.
5.The tolerance principle
Your design should be flexible and tolerant, reducing the cost of mistakes and misuse by allowing undoing and redoing, while also preventing errors wherever possible by tolerating varied inputs and sequences and by interpreting all reasonable actions reasonable.
Users don’t like making choices.
- Think well about defaults.
Users do not only like making choices but also do not like doing extra work. Using the UI forms where you might have an opportunity to have some fields pre-chosen or filled out can help users interact with your product and contribute to the business goals achievement. - Do not provide unnecessary options.
If you give your users, the opportunity to choose. Make sure all options are necessary and/or provide some business value.
6.The reuse principle
Your design should reuse internal and external components and behaviors, maintaining consistency with purpose rather than merely arbitrary consistency, thus reducing the need for users to rethink and remember.
Users don’t like being frightened.
- Make sure the system communicates with users and tells them what’s happening.
It isn’t good when a user doesn’t understand what is going on and how to go forward or back. Use various UI elements to show the status of the task and/or progress of some process. Display the error and notify how to eliminate it. - Always display the location and give the opportunity to go back.
Familiar UI elements and patterns that give the information of the user’s location and explain how to go back help reduce their frustration. Make sure users understand how to exactly navigate. - Use the “forgiveness” principle.
It’s good when the interface can prevent some of the user’s errors and gives the opportunity to cancel wrong actions. Give users features like confirmation/cancellation, save and edit later, display the tips (in some cases) etc.
A good user interface design leans on three perfectly balanced pillars: attractiveness, usability and high-level business performance.
Some of these principles are often neglected and we all face the examples of:
- Amazing looking but nearly impossible to use websites and mobile applications;
- Very complex and multi-component business applications that help provide high performance but doestn’t look that good.
User interface design is a very complicated thing that requires a lot of knowledge, experience and making researches. Following certain rules and main principles can make it easier. Remembering the goals to produce software products that are attractive and user-friendly.
130,380 total views, 3 views today
Design
Haptic technology its potential to enhance user experience

Haptic technology refers to technology that provides tactile feedback to users, allowing them to interact with digital devices and environments in a more immersive and intuitive way. Haptic technology is based on the sense of touch and uses vibration, pressure, or other physical stimuli to convey information and sensations to the user. This can range from simple vibrations in response to touch input on a smartphone screen to complex, multidimensional haptic feedback in virtual reality or gaming applications.
The goal of haptic technology is to create a more natural and intuitive interaction between people and technology, allowing users to “feel” the digital world in a way that mimics the physical world. Haptic technology is used in a variety of devices and applications, including smartphones, game controllers, wearable devices, and medical devices, among others. In virtual reality and augmented reality applications, haptic technology can be used to simulate the feeling of touching virtual objects and environments, making the experience more immersive and believable.
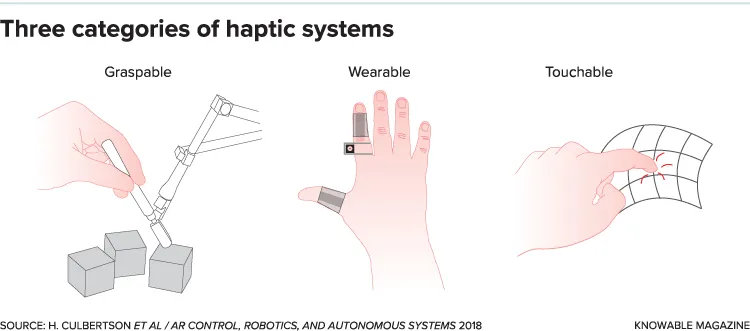
Haptic technology is still an emerging field, and there is ongoing research and development aimed at improving the accuracy, versatility, and durability of haptic devices. As technology continues to advance, it is likely that haptic technology will become increasingly integrated into a wide range of devices and applications.
Haptic technology has the potential to significantly impact various industries and immersive experiences. Some of the ways in which haptic technology is being used or has the potential to be used include:
- Gaming and Virtual Reality: Haptic technology can enhance the realism of gaming and virtual reality experiences by allowing players to feel the impact of explosions, collisions, and other events in real-time.
- Smartphones and Wearables: Haptic technology is commonly used in smartphones and wearables to provide tactile feedback for touch inputs, such as tapping or scrolling. This enhances the overall user experience and makes it easier for people to use these devices.
- Healthcare: Haptic technology is being used in the healthcare industry for rehabilitation and prosthetics, allowing patients to experience touch sensations in a controlled and precise manner.
- Automotive: Haptic technology is being used in the automotive industry to enhance the driving experience. For example, haptic feedback can be used to alert drivers to safety warnings, such as lane departure warnings, or to provide a more immersive experience when using in-car entertainment systems.
- Manufacturing: Haptic technology is being used in the manufacturing industry to provide workers with information and feedback in real-time, allowing them to work more efficiently and safely.
The use of haptic technology has the potential to greatly enhance the user experience in a wide range of industries and immersive experiences, making interactions with digital devices and environments more intuitive, engaging, and realistic.
2,941 total views, 19 views today
Design
Trends of UX 2023

User experience (UX) is a rapidly evolving field that is constantly influenced by new technologies and trends. As we move into 2023, there are a number of key trends that are expected to shape the field of UX. The field of user experience (UX) is constantly evolving, and new trends and technologies are emerging all the time. Here are a few trends that are expected to be prevalent in 2023:
- Emphasis on Empathy: With the increasing awareness of mental health and well-being, there is a growing emphasis on designing products and services that take into account the emotional needs of users. This includes designing for empathy, which involves understanding and addressing the emotional needs of users. This is achieved by conducting user research and testing, using tools like user interviews and surveys, and observing users’ behavior and emotions as they interact with a product or service.
- Human-centered design: The shift in focus towards human-centered design, which puts users at the center of the design process, will continue to be a prominent trend in 2023. This approach puts users at the center of the design process, and allows designers to create products and services that better meet the needs and goals of users. Human-centered design is achieved by conducting user research, testing, and validation to understand users’ needs, goals and pain points, and using this information to design the product or service. This approach allows designers to create products and services that better meet the needs and goals of users.
- Voice-based interfaces: With the increasing popularity of voice assistants like Alexa and Google Home, voice-based interfaces are becoming an increasingly important aspect of UX. Voice-based interfaces are also expected to become increasingly important in 2023. Voice-based interfaces are expected to be used in more products and services as a means of interaction, and designers will need to consider how to design voice-based interfaces that are intuitive, easy-to-use, and accessible to all users.
- Personalization and customization: With the rise of big data and artificial intelligence, it’s becoming increasingly possible to personalize and customize products and services to meet the needs of individual users. In 2023, we can expect to see more products and services that are tailored to the unique needs and preferences of users. With the rise of big data and artificial intelligence, it’s becoming increasingly possible to personalize and customize products and services to meet the needs of individual users. Designers will need to consider how to use data and AI to create personalized experiences that meet the unique needs and preferences of users.
- Micro-interactions: Micro-interactions, such as subtle animations and sound effects, are becoming increasingly important in creating a more engaging and satisfying user experience. In 2023, we can expect to see more products and services incorporating micro-interactions to enhance the overall user experience. Micro-interactions, such as subtle animations and sound effects, are also becoming increasingly important in creating a more engaging and satisfying user experience. In 2023, designers will need to consider how to use micro-interactions to enhance the overall user experience.
- Privacy and security: Finally, privacy and security are becoming increasingly important as users become more concerned about how their personal information is being used and protected. With the increasing concern about data privacy and security, it’s becoming increasingly important for designers to consider how products and services protect the personal information of users and how to communicate this to users in a clear and transparent way.
The field of UX is constantly evolving and designers need to keep abreast of the latest trends and technologies to create products and services that meet the needs and goals of users. By understanding and addressing the emotional needs of users, and by using human-centered design, voice-based interfaces, personalization, micro-interactions and privacy and security, designers can create products and services that provide a positive and efficient user.
3,507 total views, 19 views today
Technology
Driving the development of NLP

Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a rapidly growing field of artificial intelligence (AI) that is having a significant impact on various industries, including healthcare, technology, and lifestyle and there are some key technologies and techniques that are driving the development of NLP and are being applied in real-world applications.
One of the key technologies driving the development of NLP is deep learning. Deep learning algorithms, such as recurrent neural networks (RNNs) and transformer models, are being used to improve the accuracy and efficiency of NLP tasks, such as language translation, sentiment analysis, and text summarization. For example, RNNs and transformer models can be used to analyze large amounts of text data and identify patterns and trends that can assist in diagnoses and treatment planning in healthcare. Additionally, transformer models such as BERT and GPT-3 are used to improve the performance of virtual assistants and customer service chatbots.
Another important technology driving the development of NLP is the use of large-scale pre-trained models. Pre-trained models, such as BERT, GPT-3, and T5, have been trained on large amounts of text data and can be fine-tuned for specific NLP tasks, such as question answering and text classification. These pre-trained models have significantly improved the performance of NLP tasks and have made it easier for developers to build and deploy NLP applications. Deep learning and pre-trained models, other key technologies and techniques that are driving the development of NLP include:
- Named Entity Recognition (NER): used to identify and classify named entities, such as people, organizations, and locations, in text data.
- Part-of-Speech Tagging (POS): used to identify and classify the parts of speech, such as nouns, verbs, and adjectives, in text data.
- Sentiment Analysis: used to determine the emotional tone of text data, such as whether a piece of text is positive, negative, or neutral.
- Text Summarization: used to generate a condensed version of text data, such as a summary of a news article or a summary of customer feedback.
As the field of NLP continues to evolve, it will likely play an increasingly important role in shaping the way we live, work, and interact with technology. NLP is a rapidly growing field of AI that is having a significant impact on various industries, including healthcare, technology, and lifestyle. Key technologies and techniques, such as deep learning, pre-trained models, and NER, POS and Sentiment Analysis are driving the development of NLP and are being applied in real-world applications to improve efficiency, accuracy, and communication.
2,775 total views, 19 views today
-

 Science7 years ago
Science7 years agoHuman Cognition Processes And Types
-

 Editor's Picks7 years ago
Editor's Picks7 years agoThe Ontology of Designing Self
-

 Design9 years ago
Design9 years agoDon Norman’s Principles of Design With Examples
-

 Design8 years ago
Design8 years agoJakob Nielsen’s (Usability Heuristics): 10 Heuristic Principles With Examples
-

 Editor's Picks7 years ago
Editor's Picks7 years agoLost in the Woods
-

 Design7 years ago
Design7 years agoGamification Explained And How to Gamify Your Daily Life Part 2 of 2
-

 Editor's Picks2 years ago
Editor's Picks2 years agoSpirituality, Atheism the juxtaposition of finding meaning to purposeful life – part 2/2
-

 Art7 years ago
Art7 years agoHistory of Typography-Part 3 of 3




